- Home
- Business Overview
- Thermal Power Generation and Zero Emission Technology
Thermal Power Generation and Zero Emission Technology
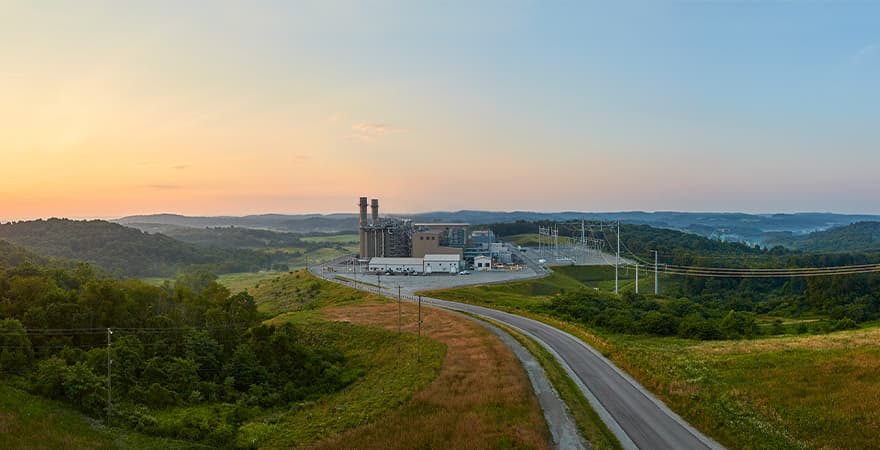

Thermal Power Generation to Fit Each Country’s Energy Needs
The J-POWER Group is involved in thermal power generation that is in accordance with regional energy needs. In the United States and Thailand, the Group participates in gas-fired power projects that leverage abundant gas resources and has been supplying electricity for more than 20 years. The Group applies the knowledge gained through these projects to expand business opportunities.
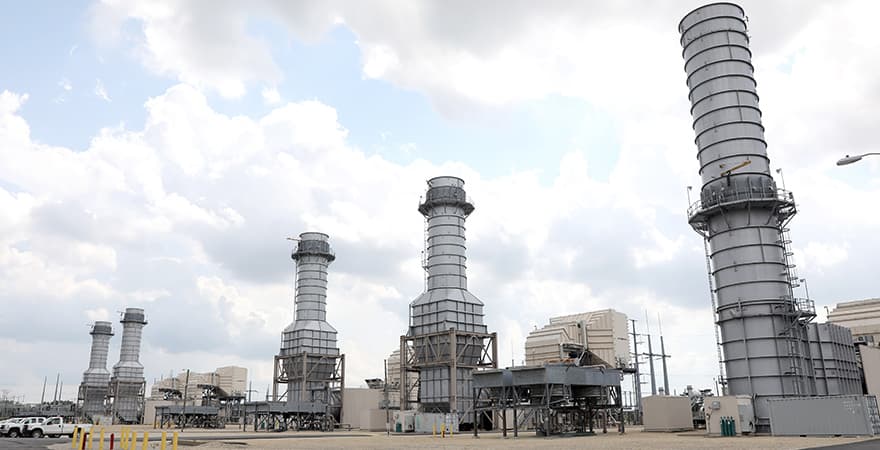

Baseload Power Source and Zero-Emission Thermal Power
In Japan, the J-POWER Group provides a stable supply of energy and reduces environmental impact through efficient coal-fired power generation. Because coal is found throughout the world, its geopolitical risks are small. It is also easy and low-cost to store, making it important to the energy security of Japan, a country with few energy resources. The J-POWER Group uses advanced technical capabilities to limit the emission of atmospheric pollutants such as SOx and NOx, and reduces CO2 emissions with world-class power generation efficiency and mixed combustion with biomass fuels. The J-POWER Group is currently aiming to realize zero-emission thermal power by combining various options such as adding gasification equipment and adopting ammonia fuel, and is promoting technology for separation, capture and use of CO2.
Throughout the rest of Asia, thermal power generation leveraging abundant coal resources continues to play an important role. J-POWER’s zero-emission thermal power technology will contribute to the stable supply of electricity and carbon neutrality in Asia.
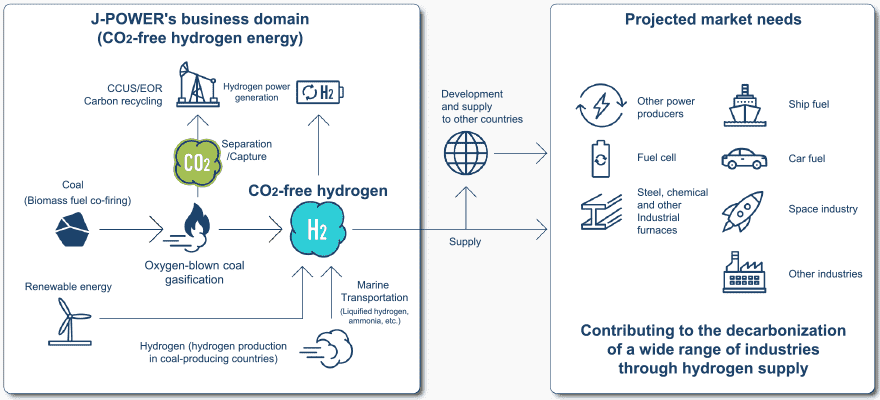
CO2-Free Hydrogen and Demonstration Testing in Japan and Overseas
The results of J-POWER’s many years of research and development of oxygen-blown coal gasification technology and CO2 separation and capture technology make hydrogen production from coal possible. The J-POWER Group is also aiming to make hydrogen CO2-free by combining technologies for effective use and storage of CO2.
Apart from actual power generation, CO2-free hydrogen can also contribute to CO2 reduction in various industrial sectors, and is a promising energy source from the standpoint of energy security for Japan and as a countermeasure against global warming.
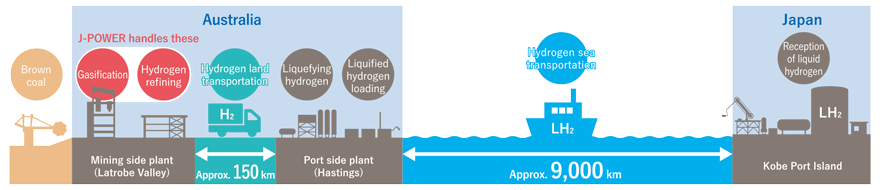
CO2-Free Hydrogen Energy Supply Chain Project in Australia
J-POWER participated in a world-first international liquid hydrogen supply chain demonstration involving the production of hydrogen*1 through the gasification of brown coal*2 in Australia and the subsequent delivery of the hydrogen to Japan by sea using liquid hydrogen carriers. This test was completed without incident in 2022.
J-POWER undertook the gasifying of brown coal and refining of hydrogen utilizing its knowledge of coal gasification.
Based on the knowledge acquired from this test, we will engage in commercialization including the planning required for creating CO2-free hydrogen, which will involve the storage of CO2 generated during hydrogen production using CCS*3.
The hydrogen produced from Australian brown coal during this demonstration test was used in Toyota Motor Corporation’s hydrogen powered vehicle that ran in round five of the Super Taikyu (endurance) Series at Suzuka Circuit.
- 1.Sponsored by the Australian Federal Government and the Victoria State Government
- 2.NEDO assisted project
- 3.CO2 Capture and Storage
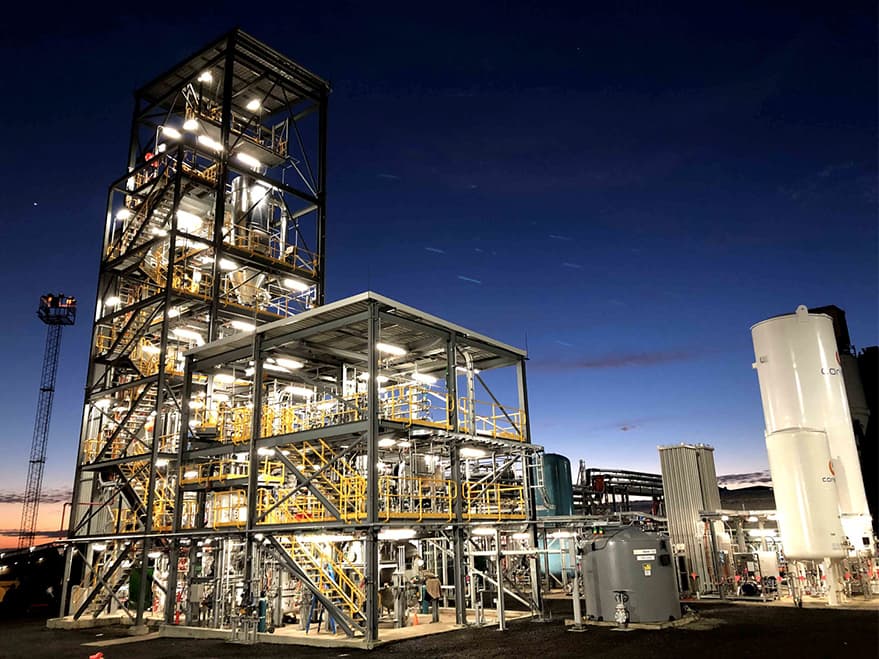

Overall view of hydrogen supply chain
Hydrogen Power Generation with Osaki CoolGen Project
The Osaki CoolGen Project*1 is a demonstration test project conducted with the aim of realizing a system that produces CO2-free hydrogen in Japan from imported coal and then using it to generate electricity. Currently, we are performing demonstration tests in stages with the aim of commercialization of oxygen-blown integrated coal gasification combined cycle technology (the combination of integrated gasification fuel cell combined cycle technology and CO2 separation and capture technologies).
In phase 1, the oxygen-blown integrated gasification combined cycle demonstration test, a high level of generation efficiency was attained using gas containing hydrogen produced from coal. Flexible load regulation was also confirmed. We have established that this is not just a base load power source, and that it is able to respond to rapid changes in renewable energy capacity requirements.
In phase 2, the demonstration test for CO2 separation and capture, basic performance (CO2 capture rate of 90% or more and captured CO2 purity of 99% or more) was confirmed through the verification tests, and this technology has achieved production and power generation with a higher level of purity for hydrogen gas.
The demonstration test period has been extended to the end of fiscal 2022, and more CO2 liquefaction equipment has been added. Also, demonstration testing has continued for CO2 separation and capture as well as the liquefaction process. Economic viability should be achieved through this sustained verification testing for reliability.
From April 2022, phase 3 began with a combined fuel cell demonstration test.
We have started the GENESIS*2 Matsushima Plan at the Matsushima Thermal Power Station (Nagasaki Prefecture), seeking to commercialize the results of the Osaki CoolGen Project through upcycling. Adding a gasification unit to the existing Matsushima Thermal Power Station Unit No. 2 makes it possible to generate electricity using gas containing hydrogen.
In addition, the power station has a system configuration that can apply proven CO2 separation and capture technology. By using the existing equipment and infrastructure, we can utilize and expand new technology while maintaining a steady supply of electric power, so we can economically and rapidly reduce CO2 emissions, and we are accelerating the realization of carbon neutrality.
- 1. Jointly conducted with the Chugoku Electric Power Co., Inc., this project is subsidized by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), a national research and development organization.
- 2. J-POWER GENESIS VISION: a project to realize carbon neutrality using CO2-free hydrogen. (Trademark applied for.)
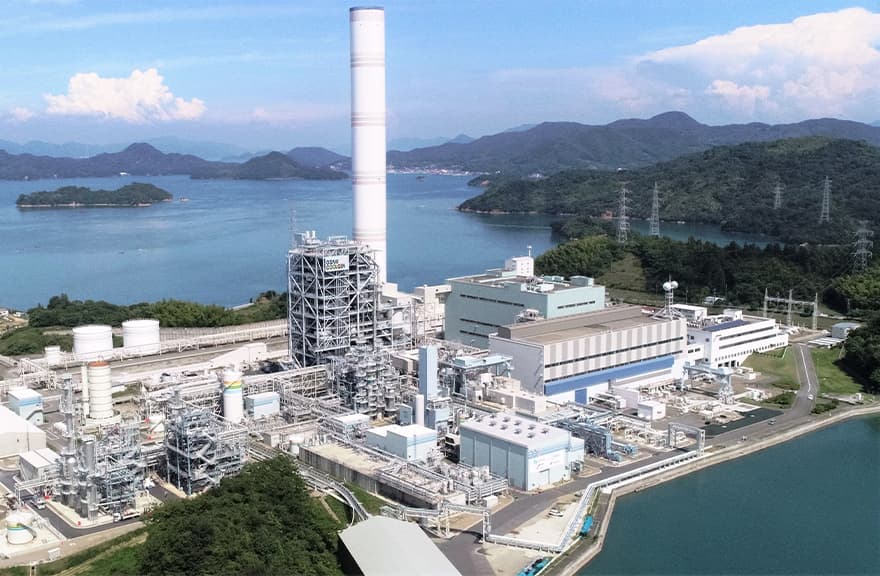

Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Technology and Carbon Recycle Technology
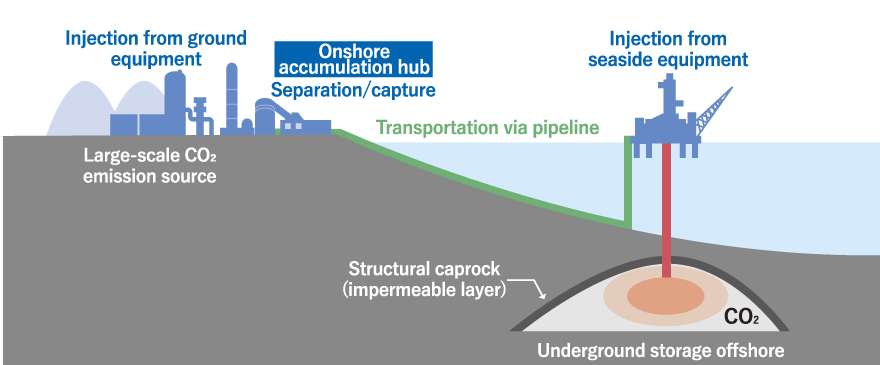
Underground storage of CO2 would make it possible to process CO2 in large amounts. The J-POWER Group has acquired knowledge through technological development and participation in demonstration tests for carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. In Indonesia, the Group has begun a feasibility study for commercialization of a CCS demonstration project in a gas field.
The Group is also exploring ways to effectively utilize the captured CO2 as a resource. Carbon dioxide is widely used in everyday life in applications such as carbonated beverages and foods, dry ice and plant growth acceleration. The Group is also considering ways to effectively use CO2 from CO2 separation and capture facilities under the Osaki CoolGen Project.
- * Joint project with J-POWER, Japan NUS Co., Ltd., and JGC Corporation. Conducted joint research with PT Pertamina and Institut Teknologi Bandung in Indonesia.
J-POWER GENESIS VISION
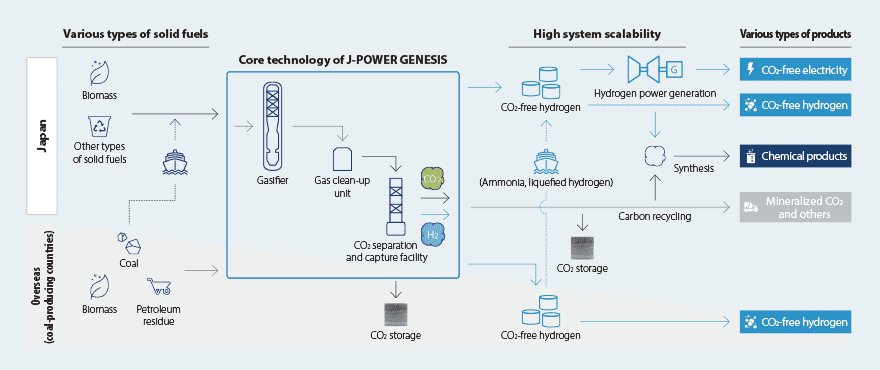
J-POWER GENESIS VISION
J-POWER is aiming to realize the J-POWER GENESIS VISION, a next-generation energy conversion system with coal gasification technology at its core. Through the application of various technologies, the system can produce a variety of products, including electricity and hydrogen from solid fuels such as coal and biomass.
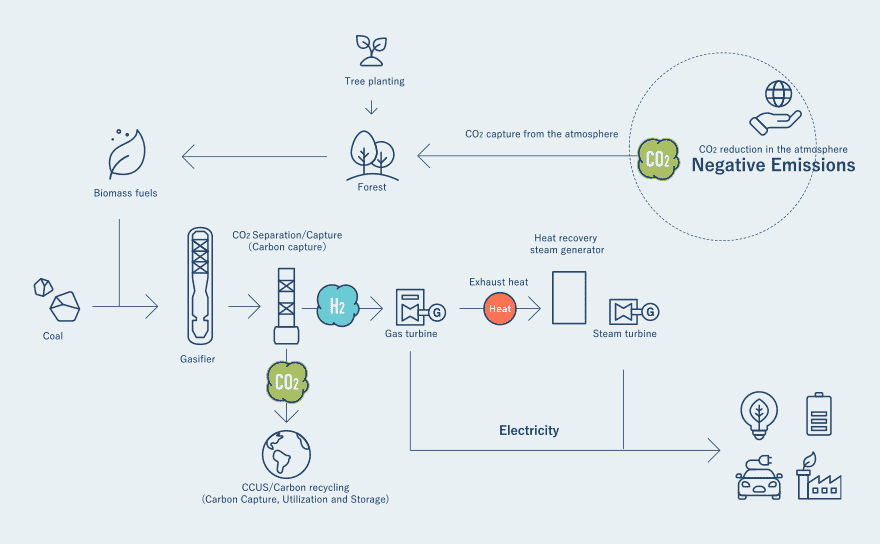
Use of Biomass Fuel and Negative Emissions
J-POWER is working to reduce CO2 emissions by applying mixed combustion of biomass fuel and coal. The Group is also engaged in the business of producing sustainable biomass fuels, such as wood fuel employing unused forest residues and carbonized sewage sludge fuel. This will aid in the creation of a circular economy.
Furthermore, it is possible to go beyond carbon neutrality to achieve “negative emissions” by combining gasification technology and CCUS technology. By gasifying biomass fuel (made from wood that absorbed atmospheric CO2 in its growth) in addition to coal and by making use of CCUS, we can not only avoid the release of CO2 but actually reduce atmospheric CO2. This is a benefit made possible by the fact that coal is a solid.
Coal Procurement
J-POWER procures fuel coal primarily from Australia and Indonesia. In Australia, the Company owns interests in three coal-mining projects through subsidiaries.
The global supply and demand of coal can vary greatly due to demand from developing countries, including China and India, trends related to energy resources other than coal, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), and other geopolitical factors. In view of this situation, J-POWER has an upstream presence with respect to the ownership of coal mines and securing diversified procurement sources to stably procure coal as fuel for thermal power generation over the long term.
