|
 |
| |
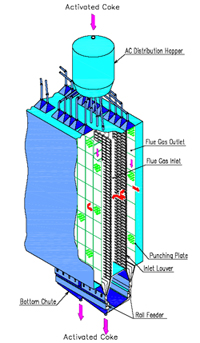 In the adsorber, the flue gas passes through a bed of activated coke (AC), while the AC moves slowly downwards at a constant flow rate. The adsorber is a single-stage or two-stage tower, depending on the design. In the adsorber, the flue gas passes through a bed of activated coke (AC), while the AC moves slowly downwards at a constant flow rate. The adsorber is a single-stage or two-stage tower, depending on the design.
Removal of SOx, NOx, mercury and particulates takes place in the adsorber as follows.
Desulfurization:
SOx is adsorbed in the form of sulfuric acid or ammonium salts on the surface of AC.
| Sulfuric acid: |
|
SO2 + 1/2O2 + H2O → H2SO4 * |
| |
|
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 * |
| Ammonium salts: |
|
H2SO4 * + NH3 → NH4HSO4 * |
| |
|
NH4HSO4 * + NH3 → (NH4)2SO4 * |
| |
|
*: Adsorption |
Denitrification:
NOx is reduced into N2 through the catalytic reaction of ammonia and AC:
| NO + NH3 + 1/4 O2 → N2 + 3/2H2O |
|
(Catalytic Reduction) |
| NO + NHxO-AC → N2 + H2O + OH-AC |
|
(Reduction on the surface of AC) |
| |
|
|
| (NHxO-AC: One of NOx reducing Compounds on the surface of the AC) |
Mercury removal:
Heavy metals such as mercury in gaseous form are adsorbed on the surface of AC. Elemental mercury are removed as efficiently as ionized and oxidized.
| Hg0 → Hg0* |
|
Hg + H2SO4 * → HgSO4 * |
| HgCL → HgCL* |
|
Hg + 1/2O2 → HgO * |
| HgCL2 → HgCL2 * |
|
HgO* + H2SO4 * → HgSO4 * |
Dust control:
The adsorber also acts as a particulate control device and keeps particulates at low level. |
| |
|
| |
|

